
Definition:
- AR:
- Enhances the real-world environment by overlaying digital information onto it. This information can include images, text, sounds, and other virtual elements.
- VR:
- Creates a fully immersive, computer-generated environment that isolates users from the real world. Users typically interact with this virtual environment using specialized equipment.
User Interaction:
- AR:
- Users can see and interact with both the real world and digital elements simultaneously. AR often relies on devices such as smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses.
- VR:
- Users are fully immersed in a virtual environment and generally cannot see the real world around them. Interaction is primarily within the virtual space using devices like VR headsets and controllers.
Environment:
- AR:
- Integrates digital elements into the existing real-world environment.
- VR:
- Creates a completely synthetic environment, detached from the real world.
Purpose and Applications:
- AR:
- Often used to enhance real-world experiences. Applications include navigation, gaming, education, and product visualization.
- VR:
- Primarily used for immersive experiences and simulations. Common applications include gaming, training simulations, and virtual tours.
Devices:
- AR:
- Devices include smartphones, tablets, AR glasses, and heads-up displays.
- VR:
- Devices range from basic VR headsets to high-end systems with motion tracking and hand controllers.
Examples:
- AR:
- Pokémon GO (AR gaming), Google Maps AR navigation, Snapchat filters.
- VR:
- Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, PlayStation VR for gaming, VR-based training simulations.
Social Interaction:
- AR:
- Often incorporates real-world social interactions. For example, users can share AR experiences through social media.
- VR:
- Can be isolating, as users are immersed in a virtual world. However, social VR platforms allow users to interact with others in the virtual space.
Realism:
- AR:
- Maintains a connection to the real world, with digital elements appearing in the context of the user’s surroundings.
- VR:
- Creates a fully artificial environment, aiming for a high level of realism within that virtual space.
Use Cases:
- AR:
- Retail shopping experiences, medical training, interactive museum exhibits.
- VR:
- Gaming, architectural visualization, virtual tourism, therapeutic applications.
While both Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality offer immersive experiences, they differ in their approach to the real world. AR enhances the real world with digital overlays, while VR creates a separate, fully immersive virtual environment. The choice between AR and VR depends on the specific use case and the desired level of immersion.
What is Mixed Reality (MR)
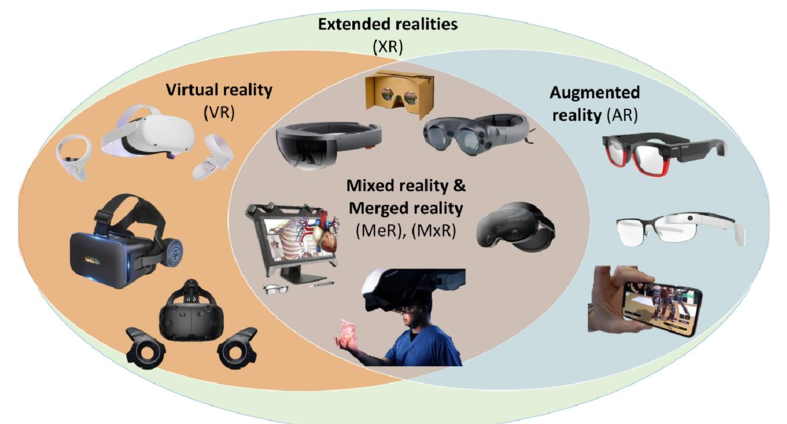
Mixed Reality (MR) is a digital environment that merges aspects of both Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). In MR, virtual and physical elements coexist and interact in real-time, creating a seamless and integrated experience that blends the real world with computer-generated content.